Notice
Recent Posts
Recent Comments
Link
| 일 | 월 | 화 | 수 | 목 | 금 | 토 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | ||||||
| 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 | 8 |
| 9 | 10 | 11 | 12 | 13 | 14 | 15 |
| 16 | 17 | 18 | 19 | 20 | 21 | 22 |
| 23 | 24 | 25 | 26 | 27 | 28 |
Tags
- SELECT 절
- 이론
- SQLD / SQLP
- 응용
- 백준
- java
- GROUP BY 절
- Python 3
- level1
- Codeup
- 기초
- Python
- 개념
- 헤드퍼스트 디자인패턴
- 파이썬
- 기본
- programmers
- pypy3
- 명품 자바 프로그래밍
- 공공데이터
- HAVING 절
- Codeforces Round #802 (Div. 2)
- Java11
- JAVA 11
- 단계별로 풀어보기
- 코딩테스트
- 자바
- 기초100제
- baekjoon
- BOJ
Archives
- Today
- Total
Development Project
[ 2021 NIPA AI - 응용 ] 4. 산업데이터를 활용한 인공지능 프로젝트 - 1. 의류 판매 상품 리뷰 분석을 통한 상품 추천 여부 예측 본문
AI/Edu
[ 2021 NIPA AI - 응용 ] 4. 산업데이터를 활용한 인공지능 프로젝트 - 1. 의류 판매 상품 리뷰 분석을 통한 상품 추천 여부 예측
나를 위한 시간 2021. 12. 17. 12:53
데이터 출처 : https://www.kaggle.com/nicapotato/womens-ecommerce-clothing-reviews
Women's E-Commerce Clothing Reviews
23,000 Customer Reviews and Ratings
www.kaggle.com
[Project 1] 의류 판매 상품 리뷰 분석을 통한 상품 추천 여부 예측
- 데이터 읽기
- 데이터 불러오기
- import
-
import numpy as np import pandas as pd import matplotlib.pyplot as plt import seaborn as sns
-
- 불러오기 [ read_csv("경로") ]
-
# Womens Clothing E-Commerce Reviews(수정).csv 데이터를 pandas를 사용하여 dataframe 형태로 불러옵니다. df_origin = pd.read_csv("./data/Womens Clothing E-Commerce Reviews(수정).csv")
-
- 정보 출력 [ .head() / .info() / .describe() ]
-
# 5개의 데이터 샘플을 출력합니다. df_origin.head()
-
# dataframe의 정보를 요약해서 출력합니다. df_origin.info()
-
# 수치형 변수의 데이터 정보를 요약하여 출력합니다. df_origin.describe()
-
- import
- 데이터 불러오기
- 데이터 정제
- 결측값 확인
- 컬럼 삭제
-
# 결측값을 처리하기 전에, 의미 없는 변수인 'Unnamed: 0, Unnamed: 0.1'를 삭제 df_clean = df_origin.drop(columns = ['Unnamed: 0', 'Unnamed: 0.1']) # 결측값 정보를 출력. 해당 변수마다 결측값의 개수 df_clean.isnull().sum()
-
# 아래 3개의 변수들의 결측값 정보를 알기위해 그 데이터들을 출력 df_clean[df_clean['Division Name'].isnull()]
-
- 컬럼 삭제
- 결측값 처리
-
# 결측값이 아닌 부분을 골라내어 df_clasn에 저장 df_clean = df_clean[~df_clean['Review Text'].isnull()] # 결측값 정보를 출력 df_clean.isnull().sum()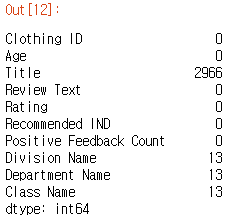
-
- 결측값 확인
- 데이터 시각화
- Title word cloud
- import
-
import nltk from nltk.corpus import stopwords from nltk import sent_tokenize, word_tokenize from wordcloud import WordCloud, STOPWORDS, ImageColorGenerator from collections import Counter from nltk.tokenize import RegexpTokenizer import re
-
- word cloud 보일 단어 출력
-
# 'Title'의 결측값을 삭제 df_clean_title = df_clean[~df_clean['Title'].isnull()] # findall 함수를 사용하여 띄어 쓰기 단위로 글자만 get(소문자로 변환도 수행) tokens = re.findall("[\w']+", df_clean_title['Title'].str.lower().str.cat(sep=' ')) # nltk에서 지원하는 'stopwords'를 다운 nltk.download('stopwords') # 영어 'stopwords'를 가져옵니다. en_stops = set(stopwords.words('english')) # tokens에서 'stopwords'에 해당되지 않는 단어를 골라내어 filtered_sentence에 저장 filtered_sentence = [token for token in tokens if not token in en_stops]
-
- word cloud 출력
# 출력 사이즈를 설정 plt.rcParams['figure.figsize'] = (16, 16) # wordcloud를 저장 wordcloud = WordCloud(max_font_size=50, max_words=100,background_color="white").generate(' '.join(filtered_sentence)) # wordcloud를 출력 plt.imshow(wordcloud,interpolation="bilinear") plt.axis("off") plt.show()
- import
- Review Text word cloud
-
# findall 함수를 사용하여 띄어 쓰기 단위로 글자만을 가져옵니다.(소문자로 변환도 수행) tokens = re.findall("[\w']+", df_clean['Review Text'].str.lower().str.cat(sep=' ')) # tokens에서 'stopwords'에 해당되지 않는 단어를 골라내어 filtered_sentence에 저장합니다. filtered_sentence = [token for token in tokens if not token in en_stops] # 출력 사이즈를 설정합니다. plt.rcParams['figure.figsize'] = (16, 16) # wordcloud를 저장합니다. wordcloud = WordCloud(max_font_size=50, max_words=100, background_color="white").generate(' '.join(filtered_sentence)) # wordcloud를 출력합니다. plt.imshow(wordcloud,interpolation="bilinear") plt.axis("off") plt.show()
- Recommended IND 시각화
-
# 분포를 막대 그래프를 사용하여 출력합니다. df_clean['Recommended IND'].value_counts().plot(kind='bar') # 분포를 도수분포표로 확인합니다. df_clean['Recommended IND'].value_counts()
-
-
- Title word cloud
- 데이터 전 처리
- 자연어 전 처리 - Tfidf
-
from sklearn.feature_extraction.text import TfidfVectorizer # TfidfVectorizer을 불러옴 (stop_words 는 영어로 설정) vectorizer = TfidfVectorizer(stop_words = 'english') # 소문자화 'Review Text'데이터를 Tfidf로 변환 X = vectorizer.fit_transform(df_clean['Review Text'].str.lower()) X.shape
-
# 예측해야 할 변수 'Recommended IND' 만을 선택하여 numpy 형태로 y에 저장합니다. y = df_clean['Recommended IND'] y = y.to_numpy().ravel() # 1 차원 벡터 형태로 출력하기 위해 ravel 사용 vectorizer.get_feature_names()
-
- 학습, 테스트 데이터 분리
-
from sklearn.model_selection import train_test_split # sklearn에서 제공하는 train_test_split을 사용하여 손 쉽게 분리 가능 x_train, x_test, y_train, y_test = train_test_split(X, y, test_size = 0.2, random_state = 0)
-
- 자연어 전 처리 - Tfidf
- 머신러닝 모델 학습
- 기본 분류 모델 학습 - 의사결정나무
-
from sklearn.tree import DecisionTreeClassifier # 의사결정나무 DecisionTreeClassifier class를 가져 옵니다. model = DecisionTreeClassifier() # fit 함수를 사용하여 데이터를 학습합니다. model.fit(x_train, y_train)
-
# score 함수를 사용하여 모델의 성능을 출력합니다. print(model.score(x_train, y_train)) print(model.score(x_test, y_test))
-
- 다양한 분류 모델 학습
-
from sklearn.neighbors import KNeighborsClassifier from sklearn.naive_bayes import MultinomialNB from sklearn.naive_bayes import BernoulliNB from sklearn.ensemble import RandomForestClassifier from sklearn.svm import SVC import xgboost as xgb from xgboost.sklearn import XGBClassifier models = [] models.append(('KNN', KNeighborsClassifier())) # KNN 모델 models.append(('NB-M', MultinomialNB())) # 멀티노미얼 나이브 베이즈 models.append(('NB-B', BernoulliNB())) # 베르누이 나이브 베이즈 모델 models.append(('RF', RandomForestClassifier())) # 랜덤포레스트 모델 (의사결정나무 확장판) models.append(('SVM', SVC(gamma='auto'))) # SVM 모델 models.append(('XGB', XGBClassifier())) # XGB 모델 for name, model in models: model.fit(x_train, y_train) msg = "%s - train_score : %f, test score : %f" % (name, model.score(x_train, y_train), model.score(x_test, y_test)) print(msg)
-
# xgb 모델에서 변수 중요도를 출력합니다. max_num_features = 20 ax = xgb.plot_importance(models[-1][1], height = 1, grid = True, importance_type = 'gain', show_values = False, max_num_features = max_num_features) ytick = ax.get_yticklabels() word_importance = [] for i in range(max_num_features): word_importance.append(vectorizer.get_feature_names()[int(ytick[i].get_text().split('f')[1])]) ax.set_yticklabels(word_importance) plt.rcParams['figure.figsize'] = (10, 15) plt.xlabel('The F-Score for each features') plt.ylabel('Importances') plt.show()
-
- 기본 분류 모델 학습 - 의사결정나무
- 평가 및 예측
- Confusion Matrix
-
from sklearn.metrics import confusion_matrix # 의사결정나무 모델에 confusion matrix를 사용하기 위하여 테스트 데이터의 예측값을 저장 model_predition = model.predict(x_test) # sklearn에서 제공하는 confusion_matrix를 사용 cm = confusion_matrix(y_test, model_predition) # 출력 파트 - seaborn의 heatmap을 사용 plt.rcParams['figure.figsize'] = (5, 5) sns.set(style = 'dark', font_scale = 1.4) ax = sns.heatmap(cm, annot=True) plt.xlabel('Real Data') plt.ylabel('Prediction') plt.show() cm
-
- Precision & Recall
-
from sklearn.metrics import recall_score from sklearn.metrics import precision_score # sklearn에서 제공하는 recall_score, precision_score를 사용하여 recall과 precision 결과물을 출력합니다. print("Recall score: {}".format(recall_score(y_test, model_predition))) print("Precision score: {}".format(precision_score(y_test, model_predition)))
-
- 테스트 데이터의 예측값 출력
-
# 0번부터 4번까지 5개를 출력해보겠습니다. for i in range(5): # 의사결정나무 모델을 사용하였습니다. prediction = model.predict(x_test[i]) print("{} 번째 테스트 데이터 문장: \n{}".format(i, df_clean['Review Text'][i])) print("{} 번째 테스트 데이터의 예측 결과: {}, 실제 데이터: {}\n".format(i, prediction[0], y_test[i]))
-
- Confusion Matrix
'AI > Edu' 카테고리의 다른 글
Comments




